Melexis recently announced a new thermographic sensor , the MLX90642. With onboard calibration and a digital I 2 C interface, this new sensor may support system designers in applications requiring non-contact temperature measurements.
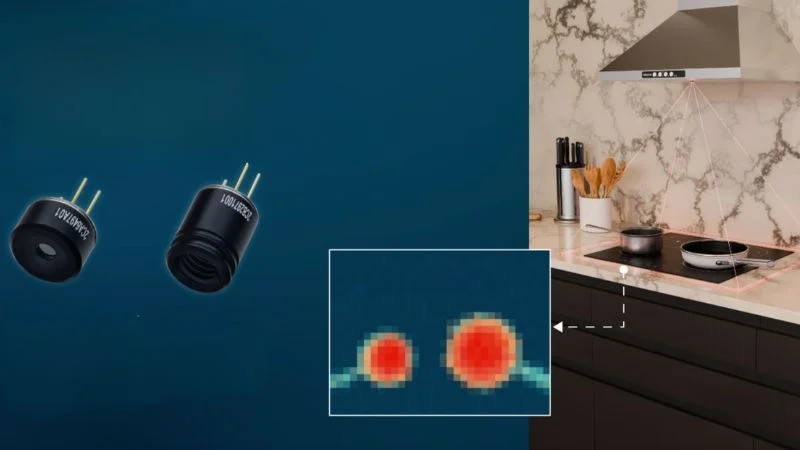

The MLX90642.
Non-contact thermal sensors are generally used in consumer goods like microwave ovens and building air conditioning. These sensors are also useful in industrial settings, maintaining safe manufacturing processes or equipment upkeep. Combined with machine vision, temperature sensors can also provide new insights into people and movement detection. Melexis designed its new MLX90642 thermographic sensor (link downloads datasheet) to improve signal-to-noise ratio, global shutter readout, and onboard temperature calculation for applications ranging from smart cooking to hotspot localization.
A Thermography Sensor With Better SNR
The MLX90642 operates as a 32 x 24 thermal infrared (IR) array, providing a total of 768 pixels for detailed thermal imaging. The sensor runs on a 3.3 V supply voltage with a nominal current consumption of 28 mA and an ambient temperature range from -40°C to 85°C. Without any contact, the device can detect object temperatures from -40°C to 260°C, allowing it to fulfill certain safety requirements.
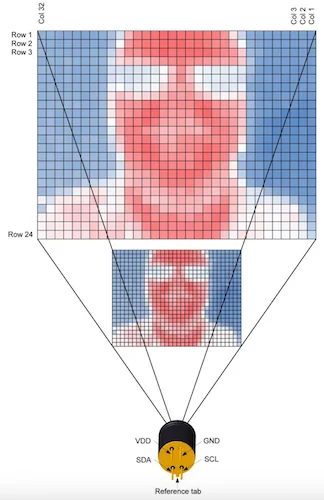
The MLX90642's pixel arrangement in the FOV.
Melexis claims that the MLX90642 has an improved signal-to-noise ratio that surpasses existing solutions. Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference (NETD) is often used as a metric for a temperature sensor’s SNR performance. NETD, also known as “thermal contrast,” is measured in milli-Kelvin (mK). It indicates the smallest measurable temperature difference on the sensor. Any noise ranging above that value would be unresolved. For example, a sensor with a NETD of 1 mK would not be able to resolve a 2-mK background. A pixel reading can either capture noise or temperature from the object. Thus, a lower NETD results in better temperature sensing.
The MLX90642 is rated with a NETD of 65 mK at a 2 Hz refresh rate. Its lower NETD at a higher refresh rate may enable more accurate readings.
FOV Options Enable Design Trade-Offs
The MLX90642 comes with two FOV options available for purchase. The options are distinguishable by a -BCA or a -BCB product code. The BCA provides a wide FOV at 110°x75°. The BCB versions have a smaller FOV of 45° x 35°.
Depending on the version, the pixels of the sensors are divided into zones, each with varying levels of accuracy. The BCA sensors have four zones, while the BCB sensors have two zones. These options allow system designers to choose between performance and field of view based on their application requirements.
Onboard Digital Features for Simple Integration
Melexis emphasizes the MLX90642's onboard capabilities and digital interfaces. The MLX90642 calculates temperature onboard, eliminating the need for an external MCU. The MLX90642 comes in a four-pin TO39 package with a digital I2C interface. The sensor can output linearized object temperature (To), raw IR data, and ambient temperature (Ta) stored in its onboard RAM.
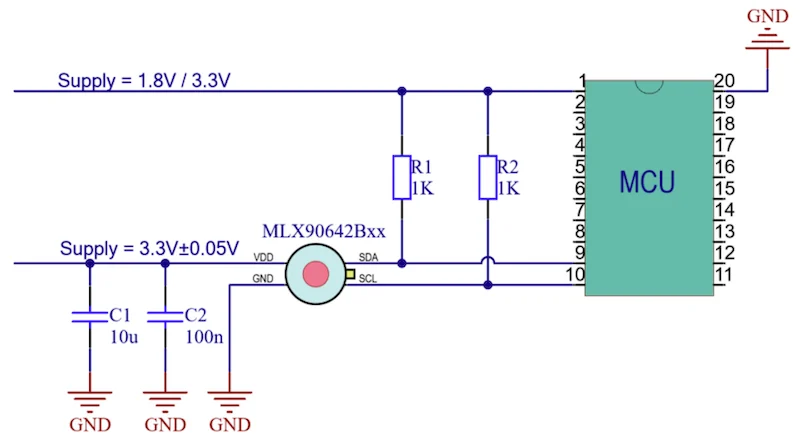
Melexis' recommended application diagram of the MLX90642.
The MLX90642’s internal registers can be accessed to monitor the sensor’s progress. It can be set to continuous, step, sync request, or sleep modes. Several configurable parameters can be modified using a configuration command. The MLX90642 is equipped with a programmable refresh rate from 2 Hz to 16 Hz. Designers can choose to opt for more FPS at the cost of worse noise performance. Users can also request a global shutter readout for the full raw image. Emissivity and background temperature can be calibrated to further improve readings based on the application.
The MLX90642 is available for purchase. Evaluation boards and code libraries are also available for system designers considering this IC.
 English
English
